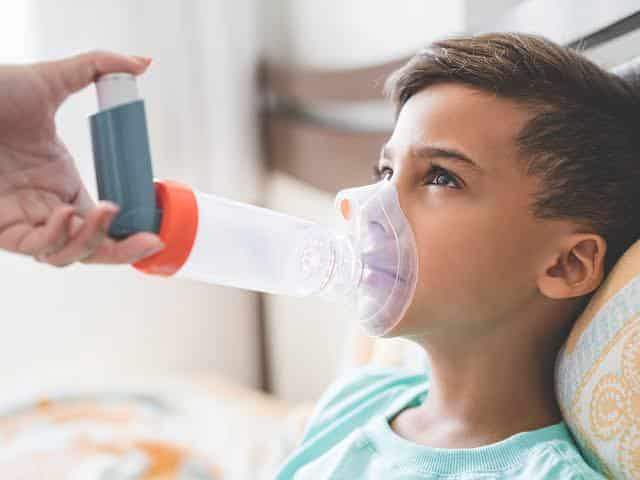
When air pollution levels are high, it’s especially important for parents to take extra precautions to protect their children, as their developing bodies are more vulnerable to the harmful effects of polluted air. Here’s what parents should know about managing care during air pollution:
1. **Health Risks of Air Pollution for Children**
– **Respiratory Problems**: Children are more likely to develop asthma, bronchitis, and other respiratory issues due to exposure to polluted air.
– **Increased Vulnerability**: Young children breathe more air (and more pollutants) relative to their size, and their lungs are still developing.
– **Long-term Effects**: Chronic exposure to polluted air can lead to long-term health problems, including impaired lung development and increased risk of cardiovascular diseases.
2. **Monitor Air Quality**
– **Check Air Quality Index (AQI)**: Stay updated on the Air Quality Index (AQI) in your area, especially during days when pollution is high. Various apps and websites provide real-time AQI data.
– **Know the Pollution Sources**: Pollution may come from traffic, industrial emissions, wildfires, or weather patterns. During high-pollution days (such as during wildfire season or smog), take extra caution.
3. **Reduce Outdoor Exposure**
– **Limit Outdoor Activities**: On days with high pollution, limit outdoor play or sports, especially for children with asthma or preexisting respiratory conditions. If outside activities are unavoidable, try to do them during times when pollution levels are lower (often early morning or late evening).
– **Indoor Alternatives**: Encourage indoor play or exercise when pollution levels are high. Activities like reading, art, or board games can keep children engaged inside.
4. **Ensure Good Indoor Air Quality**
– **Keep Windows Closed**: On high-pollution days, keep windows and doors closed to prevent outdoor pollutants from entering the home.
– **Ventilate When Safe**: If outdoor air quality improves, ventilate your home by opening windows briefly to refresh the air inside.
5. Health Precautions for Sensitive Children**
– **Asthma and Allergies**: If your child has asthma or allergies, follow your doctor’s advice on medication and treatment plans. In some cases, parents may need to adjust or increase the use of inhalers or other medications.
– **Monitor Symptoms**: Keep an eye out for signs of breathing difficulties (coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath) and take appropriate action if symptoms worsen.
– **Hydration and Nutrition**: Encourage children to stay hydrated and eat healthy foods that support immune and respiratory health, like fruits rich in antioxidants (e.g., apples, oranges).
6. **Signs of Trouble and When to Seek Medical Help**
– **Breathing Issues**: If your child shows signs of shortness of breath, persistent coughing, or unusual fatigue during or after exposure to polluted air, seek medical advice.
– **Asthma Attacks**: If your child has an asthma attack, follow the prescribed emergency treatment (e.g., inhaler use) and seek medical help if symptoms don’t improve.
7. **Educate Children About the Risks**
– **Awareness**: Teach older children about the dangers of air pollution and encourage them to avoid outdoor activities when pollution levels are high.
– **Safe Habits**: Explain the importance of avoiding strenuous exercise outside on polluted days and encourage wearing protective masks if necessary (though consult a healthcare provider before using masks for children).
By taking these precautions, parents can help minimize the harmful effects of air pollution on their children’s health, particularly during times of high pollution.